What is Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition in which level of glucose (sugar) in the blood is high. The body produces insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, which breaks down the sugar consumed in food. A reduction in the production and / or utilization of insulin causes diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
In this type, the body completely stops producing insulin due to the destruction of insulin producing pancreatic cells by the body’s immune system. Usually seen in children and young adults.
Type 2 Diabetes
This is the more common type of Diabetes. In this, the pancreas either produces an inadequate amount of insulin or the body is unable to use the available insulin properly. Heredity, stress, sedentary lifestyle and obesity are common triggers of type 2 Diabetes. It has to be managed with anti-diabetic medication, regular monitoring, diet and lifestyle modifications.
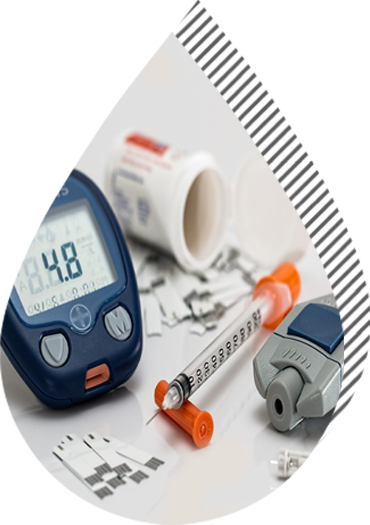
Complications
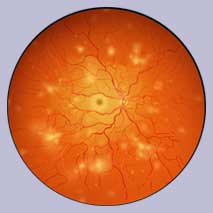
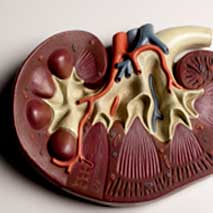
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to complications over a period of time. Primarily it affects the eyes (retinopathy), kidneys (nephropathy), nerves (neuropathy), heart and blood vessels (PVD, myocardial infarction) and brain (stroke).
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or low blood sugar is the most common complication in individuals with diabetes. Common causes are vigorous physical activity, wrong dose of insulin / antidiabetic medicine, not eating enough or eating too late.
Symptoms – discomfort, sweating, palpitations, weakness and giddiness, excessive hunger.
Services we offer
Iva Speciality Clinic offers a wide range of services focused on complete diabetes care.




Patients Consulted
Years of Experience
Diet & Lifestyle management
Simple lifestyle changes can help in preventing or delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes
- Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight
- Be physically active - atleast 30 minutes of regular, moderate intensity activity on most days
- Eat a healthy diet of between 3 to 5 servings of fruit and vegetables a day and reduce intake of sugar and saturated fats
- Avoid smoking, chewing tobacco and harmful use of alcohol
- Manage stress
- Test blood glucose and glycated haemoglobin levels regularly - HbA1C
Looking for more information ?